Financial derivatives are complex financial instruments whose value is derived from the value of an underlying asset, index, or rate. These instruments play a crucial role in modern financial markets, allowing investors to hedge risk, speculate on price movements, and enhance portfolio returns. This document explores the various types of financial derivatives, their applications, and the risks associated with them.
What are Futures?
Futures are standardized contracts that obligate the buyer to purchase, and the seller to sell, an asset at a predetermined price at a specified time in the future. These contracts are traded on exchanges and are commonly used for hedging against price fluctuations in commodities, currencies, and financial instruments or financial derivative’s.
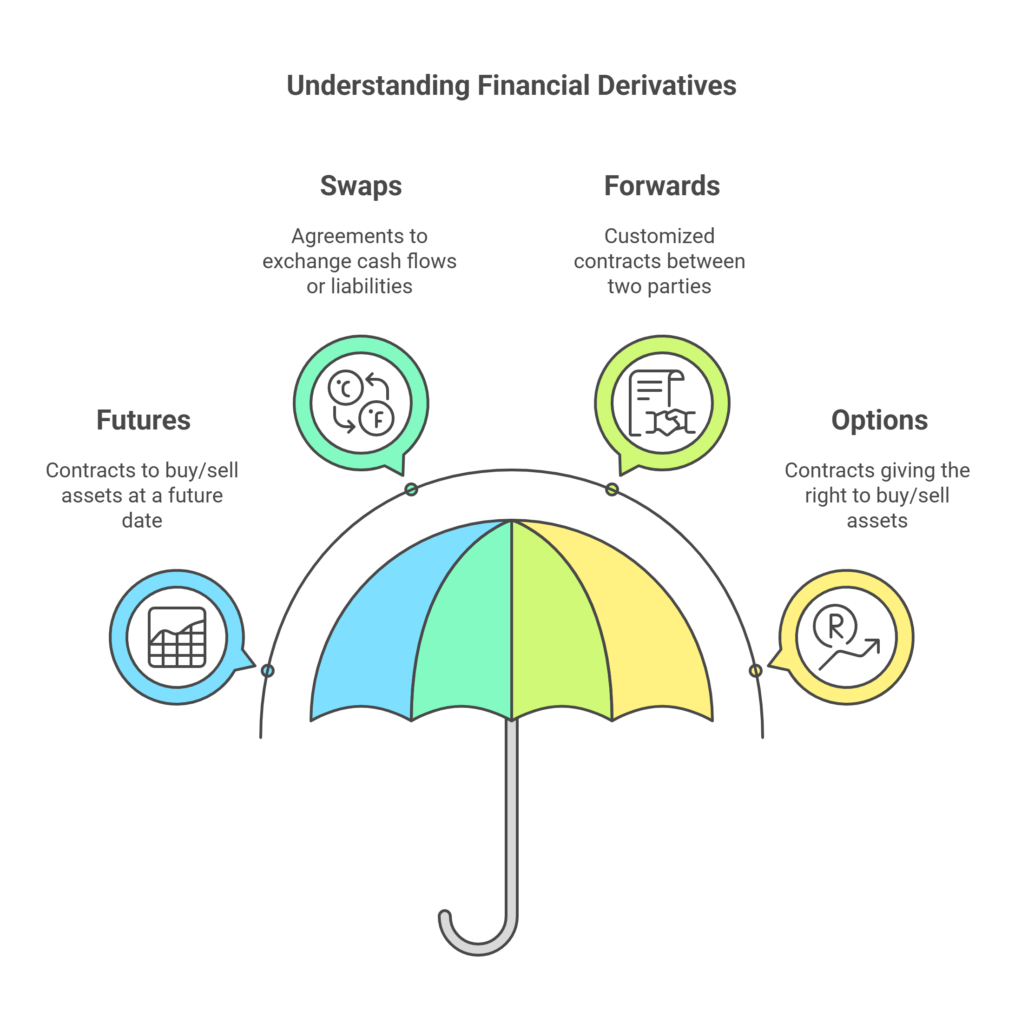
What are Financial Derivatives?
Financial derivatives are contracts whose value is derived from the performance of an underlying asset, index, or rate. They are primarily used for hedging risk or for speculative purposes. The main types of derivatives include futures, swaps, forwards, and options, each serving different purposes and having unique characteristics FINANCIAL DERIVATIVES
Futures
Futures are standardized contracts traded on exchanges that obligate the buyer to purchase, and the seller to sell, an asset at a predetermined price at a specified future date. They are commonly used for commodities, currencies, and financial instruments.
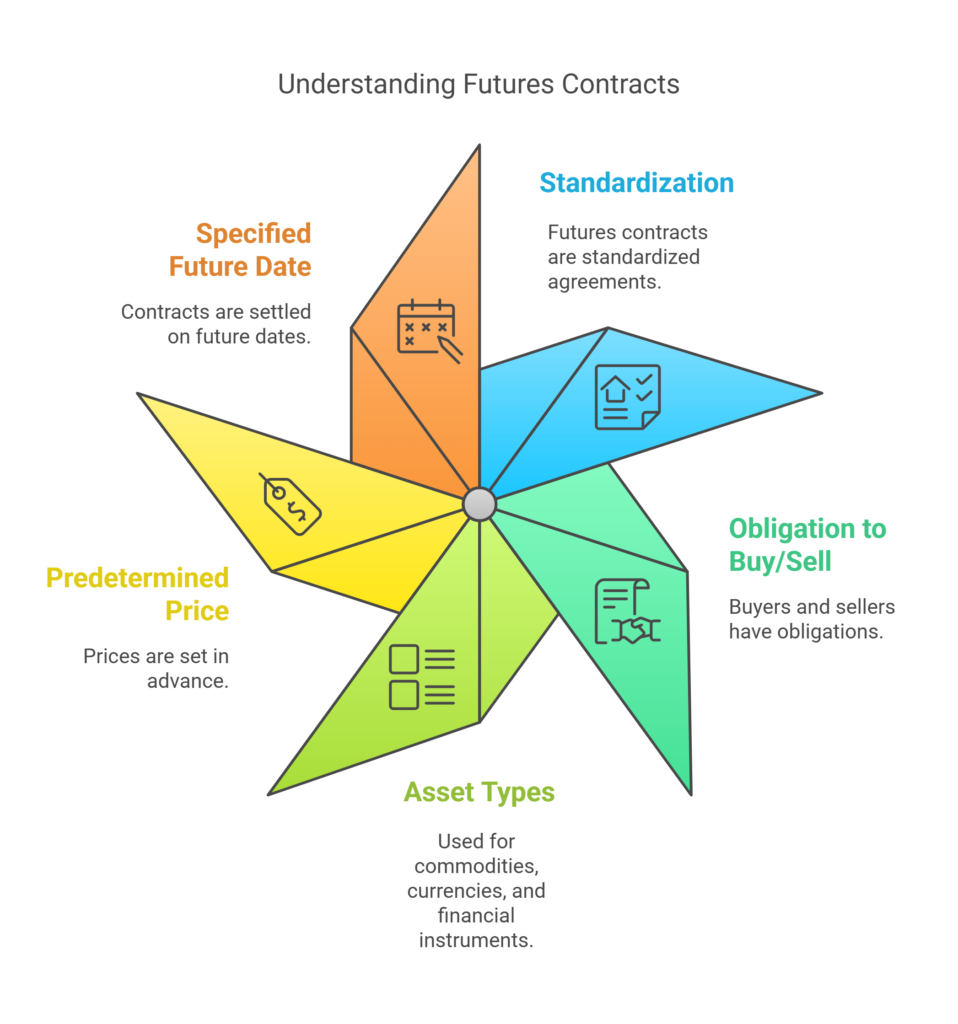
Key Features of Futures:
- Standardization: Futures contracts are standardized in terms of quantity and quality, making them easily tradable on exchanges.
- Margin Requirements: Traders must maintain a margin account, which is a percentage of the contract’s value, to cover potential losses.
- Settlement: Futures can be settled in cash or through physical delivery of the underlying asset.
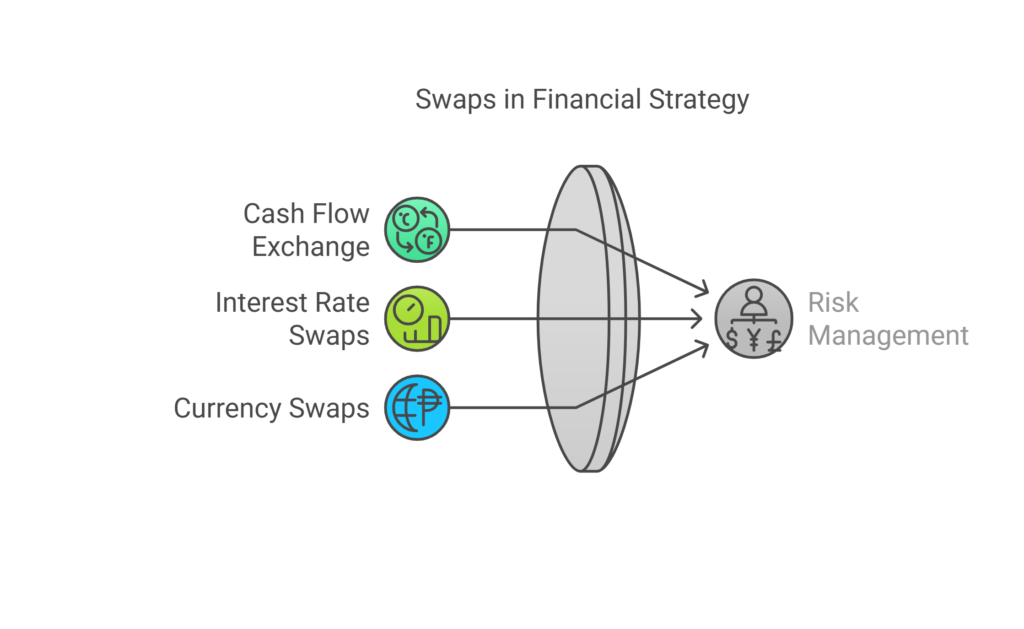
Swaps
Swaps are financial agreements between two parties to exchange cash flows or financial instruments over a specified period. The most common types of swaps are interest rate swaps and currency swaps.
Key Features of Swaps:
Counterparty Risk: Swaps involve the risk that one party may default on its obligations.
Customization: Swaps can be tailored to meet the specific needs of the parties involved.
Hedging: They are often used to hedge against interest rate risk or currency fluctuations.
Key Features of Swaps:
- Customization: Swaps can be tailored to meet the specific needs of the parties involved.
- Counterparty Risk: Since swaps are typically over-the-counter (OTC) agreements, they carry the risk of default by one of the parties.
- Market Risk: The risk of losses due to adverse price movements in the underlying asset.
Forwards
Forwards are similar to futures but are not standardized and are traded OTC. They involve an agreement to buy or sell an asset at a specified price on a future date.
Key Features of Forwards:
- Customization: Forwards can be customized in terms of quantity, quality, and delivery date.
- No Margin Requirements: Unlike futures, forwards do not require margin accounts, but they do carry counterparty risk.
Options
Options are contracts that give the holder the right, but not the obligation, to buy or sell an asset at a predetermined price before or at the expiration date. They are widely used for hedging and speculative purposes.
Types of Options:
- Call Options: Give the holder the right to buy the underlying asset.
- Put Options: Give the holder the right to sell the underlying asset.
Key Features of Options:
- Premium: The buyer of an option pays a premium to the seller for the rights granted by the option.
- Expiration: Options have a limited lifespan and expire on a specific date.
Conclusion
Financial derivatives such as futures, swaps, forwards, and options are essential tools in the financial markets. They provide opportunities for risk management and speculation, but they also come with inherent risks. Understanding these instruments is crucial for anyone looking to navigate the complexities of modern finance derivative’s effectively.